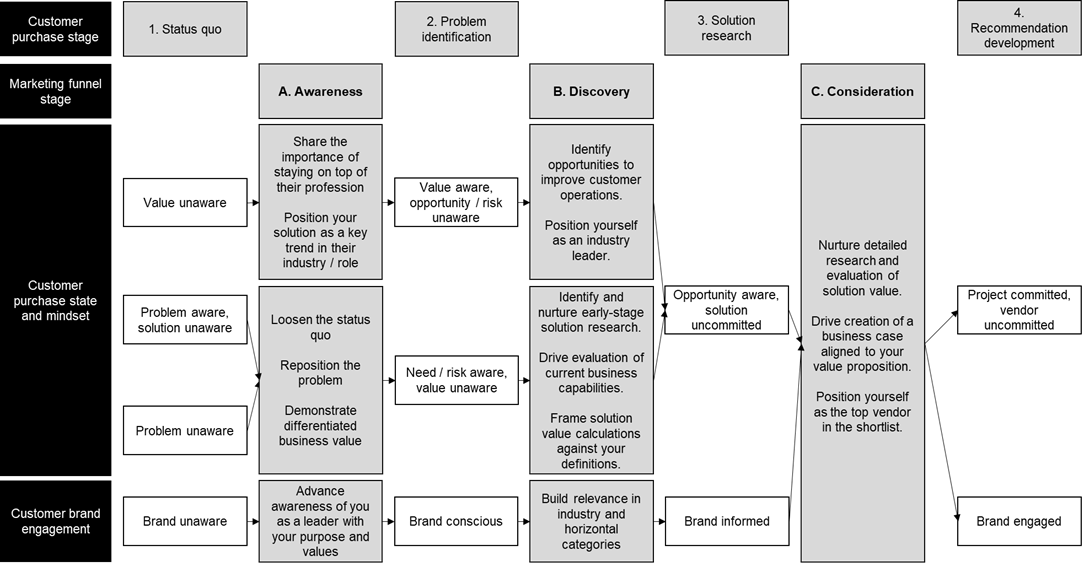
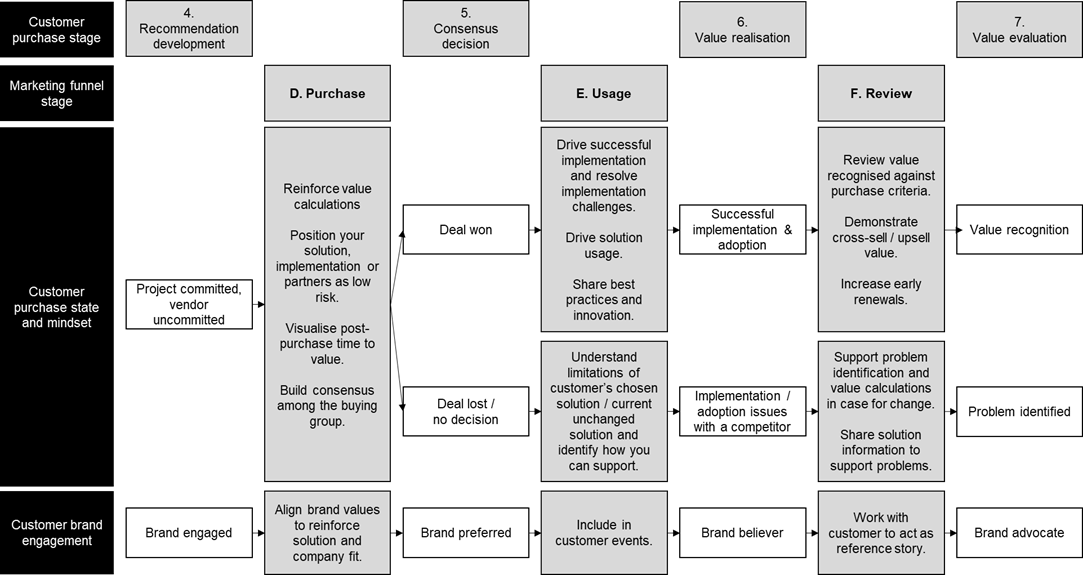
3.4 Marketing funnel stages
Within the niche world of physics-based jokes there is a class that all end with the punchline “assume a spherical chicken”. A 1973 edition of Science Magazine included the following example, attributed to Steven D Stellman of Princeton University. “A certain commercial farm was having great difficulty raising its egg productivity. Every suggestion they attempted failed to increase the output of its hens. For one year they tried special feed formula, hormones, minerals in the hen’s drinking water, piped-in music (rock and classical), soft lights, ambient temperature variation, and even specially imported roosters, all with the same notable lack of success. In desperation, they finally took the suggestion of an extension officer to hire a theoretical physicist. After three more months of agonized waiting, the theoretician announced to the anxious farmers that he had a solution to their egg problem. He strode up to the blackboard and confidently began ‘Postulate a spherical chicken…’”.
The joke here is that to a physicist the idea of modelling a real-world scenario to simplify and control variables is very natural. This makes the calculations they need to complete achievable, but in this case the simplification renders the applicability to reality highly questionable. The seven states of the customer purchase path model what every average customer will go through. One again, this is a model; we are not attempting to perfectly recreate the exact stages that a customer will go through, we are trying to create a finite, usable number of stages that can inform how we operationalise to engage them.
We are, however, trying not to create a spherical chicken. The model needs to be grounded on a useful, relevant and applicable level of detail without becoming unwieldy or overly complex to implement. Your organisation may have different insights into the way your customers buy that means you can improve upon this, but for most this is a comprehensive view that can be applied to many customers. The very nature of a customer journey framework is to simplify the complex down to a manageable, identified model of reality.
The role of sales and marketing, however, is not just to meet customers at their journey state and leave them there. The objective of buyer enablement is to move customers through their purchase experience. Every sales and marketing touchpoint should have a clear objective behind it to enable buyers to move from state A to state B. With this approach we move from a pureplay model of a customer’s journey to a marketing funnel framework that provides both a definition of the customer and a definition for how to engage said customer and move advance their purchase.
Early stage funnel:
Late stage and post-purchase:
As this model hopefully illustrates, marketing funnel stages are not the same as the customer journey states. The role of sales and marketing is to enable customers within each of those states to advance to the next, and recall that by ‘customer’ we usually mean ‘customer buying group’. Individual stakeholders within a buying group may move through this journey at different rates. You may find one stakeholder is in discovery while another recognises the problem but doesn’t think finding a solution is important.
Customers can also advance through brand engagement at different rates than through their purchase state. Typically when a customer’s purchase mindset is ahead of their brand engagement it is a sign that they may not be effectively engaged in your value proposition. Your objective must be to advance the whole buying group through the full journey.
A. Awareness
| Customer purchase state | Your objective | Using touchpoints that |
|---|---|---|
| Value unaware | Introduce your solutions and position them as a key trend in the customer's industry or function. Position your solution as the answer to current and future challenges and demonstrate how you help customers stay on top of their professions. |
|
|
Problem aware, solution unaware
Or Problem unaware |
Raise pain points that will be familiar to the audience, explore the underlying barriers standing in the way of improvement and reposition them to align to your unique strengths. Introduce your brand's thought leadership in this space and can help customers understand their problems better.
Importantly, make the status quo appear untenable in the medium to long term. |
|
| Brand unaware | Position yourself as a thought leader and trusted brand. Use stories of customer success to showcase our expertise, vision and values |
|
B. Discovery
| Customer purchase state | Your objective | Using touchpoints that |
|---|---|---|
| Value aware, opportunity / risk unaware | Educate customers on how to solve their problems with your solutions. Arm them with best practices and practical steps so that they can build a roadmap for innovation that will set them up for future success. Build awareness of the value calculations customers should use to evaluate solutions |
|
| Need, risk aware, value unaware | Emphasise the value that your solutions can uniquely drive across the customer's organisation. Motivate customers to start evaluating their current business capabilities against your unique value criteria. |
|
| Brand conscious | Showcase your ability to solve challenges within our customer's industries with relevant insight on customer challenges. |
|
C. Consideration
| Customer purchase state | Your objective | Using touchpoints that |
|---|---|---|
| Opportunity aware, solution uncommitted | Show how you lead in higher value, faster time to market and lower risk versus the competition. Evidence why you should be top of a vendor shortlist. Demonstrate how they will see value, estimate ROI and get them to buy into the value estimate. |
|
| Brand informed | Give customers the information they need to create a business case for using you. |
|
D. Purchase
| Customer purchase state | Your objective | Using touchpoints that |
|---|---|---|
| Project committed, vendor uncommitted | Reinforce the value calculations that a customer will use to make a purchase decision. Visualise specific time-to-value and the positive post-purchase experience that will facilitate it. Position your solutions as the lowest risk and highest value, and build consensus of this among the buying group. |
|
| Brand engaged | Create tangible brand experiences that bring your brand story to life across every touchpoint. Show that our values complement and reinforce our customer's values. |
|
E. Usage
| Customer purchase state | Your objective | Using touchpoints that |
|---|---|---|
| Deal won | Ensure an easy and fast adoption of the agreed solution. Support customers with the implementation aligned to the business value assessment agreed during the pre-sales process. Demonstrate how the solution is helping the customer achieve their objectives and delivering the value expected. |
|
| Deal lost / no decision | Maintain contact with the customer and understand the new pain points of the route they have chosen. Continue to offer guidance and thought leadership on unmet needs as well as presenting a roadmap for better long-term value, respectful of the customer's decision. |
|
| Brand preferred | Establish yourself as special among the customer's vendors, earning the position as a trusted partner. Remind and reinforce the breadth of your full services, capabilities and expertise. |
|
F. Review
| Customer purchase state | Your objective | Using touchpoints that |
|---|---|---|
| Successful implementation | Help customers further maximise their purchase decision by demonstrating the value of further solutions. Help them internally showcase solution value and inspire them to do more by embracing and adopting your end-to-end value vision. |
|
| Implementation / adoption issues with a competitor | Show customers how their needs can still be met with your solution. Demonstrate the limitations of their current solution and how their future needs will be unmet. |
|
| Brand believer | Support customers sharing value internally and externally by activating them as a success story. Turn customers into public-speaking advocates for you. |
|